Mr Haris Papanikolaou
Consultant Ophthalmologist
The role of the veins in the body is to drain away the used blood so that new blood with nutrients and oxygen can come and supply the tissues. When a retinal vein gets blocked then the blood cannot drain away properly. As a result swelling develops and there may also be bleeding which causes damage to the cells at the back of the eye resulting in sight loss. The extent of sight loss depends on the site of the blockage in the eye.
The loss of sight is usually gradual and painless.
Treatment for vein occlusions
While things can sometimes improve on their own, commonly treatment will be required to control the swelling at the back of the eye.
There are three treatments currently available for retinal vein occlusion: Laser treatment, steroid implant and injections with Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors (Anti-VEGF).
Laser
Laser can be used in some case of vein occlusion to help control the bleeding and swelling at the back of the eye. Sometimes the sight improves a little even though more often, laser treatment aims at reducing the risk of any further sight loss.
Sometimes as a complication of a vein occlusion abnormal vessels can start to grow at the back of the eye. These can bleed leading to further sight loss. In these cases laser can be used to seal these vessels and prevent this possible complication.
Steroid implant
A steroid implant will control the inflammation inside the eye reducing leakage from retinal vessels and therefore reducing the swelling of the retina.
The implant is delivered in the eye with an injection using a special device.
Anti VEGF injections
Anti VEGF injections will help reduce swelling of the retina. A course of injections is usually needed.
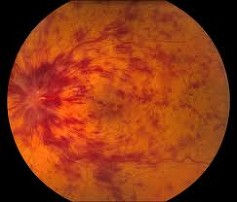

Example of Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Example of Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion